Advanced Nuclear for District Energy Webinar
Summary
Watch this on-demand webinar to explore how amid the changes and uncertainty present in utility markets, the development of advanced nuclear technologies holds great promise for resilient energy supplies. This presentation discusses how microreactors are emerging to serve the needs of district energy systems, considerations in evaluating microreactor options and barriers that must be addressed as the technology moves toward commercialization.
In this webinar, you will:
- Learn how microreactors provide low-carbon energy solutions for district energy systems.
- Understand the advantages of their compact, factory-built design and ease of deployment in various locations.
- Discover their potential to enhance energy security and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Delve into design innovations and advanced safety features of microreactors.
- Explore how microreactors can support a range of applications, from meeting urban energy needs to powering remote industrial operations.
- Gain insights into the role of microreactors in advancing decarbonization efforts and energy independence.
Webinar Q&A
- What is advanced nuclear?
- Advanced nuclear refers to a new generation of nuclear reactor technologies designed for improved safety, efficiency and responsive operation. These reactors incorporate standardized designs and advanced fuels to help overcome some of the limitations and challenges experienced in the commercial nuclear sector. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced safety. Advanced reactors use passive safety systems that don’t require human intervention or external power sources for shutdown, and the fuel cannot melt down.
- Operability. Advanced nuclear technologies provide electricity and high-quality thermal energy production.
- Higher efficiency. Microreactors are designed to use fuel more efficiently, running 8-10 years between refuels, minimizing waste.
- Modular designs. Advanced reactors are compact and modular, allowing for standardized design and ease of construction.
- Reduced environmental impact. Nuclear produces zero-emission energy, providing an important role in eliminating greenhouse gas emissions.
- Advanced nuclear refers to a new generation of nuclear reactor technologies designed for improved safety, efficiency and responsive operation. These reactors incorporate standardized designs and advanced fuels to help overcome some of the limitations and challenges experienced in the commercial nuclear sector. Key benefits include:
- Are microreactors safe?
- Yes, their design incorporates safety as a top priority. Key safety features include:
- Passive safety systems. Microreactors incorporate passive safety features that do not require operator intervention or external power for safe shutdown. The microreactor can automatically shut itself down in the event of an emergency or upset.
- Containment. Microreactors include robust containment structures to prevent the release of radioactive materials.
- Standardized design. The compact and straightforward design of microreactors minimizes the quantity of components that could potentially fail, enhancing overall safety.
- Advanced fuel. Microreactors use efficient high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) fuel encased in matrix materials that withstand extremely high temperatures, preventing the potential for meltdown.
- Remote operation. Microreactors can be operated remotely, reducing the risk of operator error.
- Regulatory oversight. Similar to all nuclear technologies, microreactors are subject to rigorous regulatory licensing and oversight approvals.
- Yes, their design incorporates safety as a top priority. Key safety features include:
- How can a microreactor benefit a district energy system?
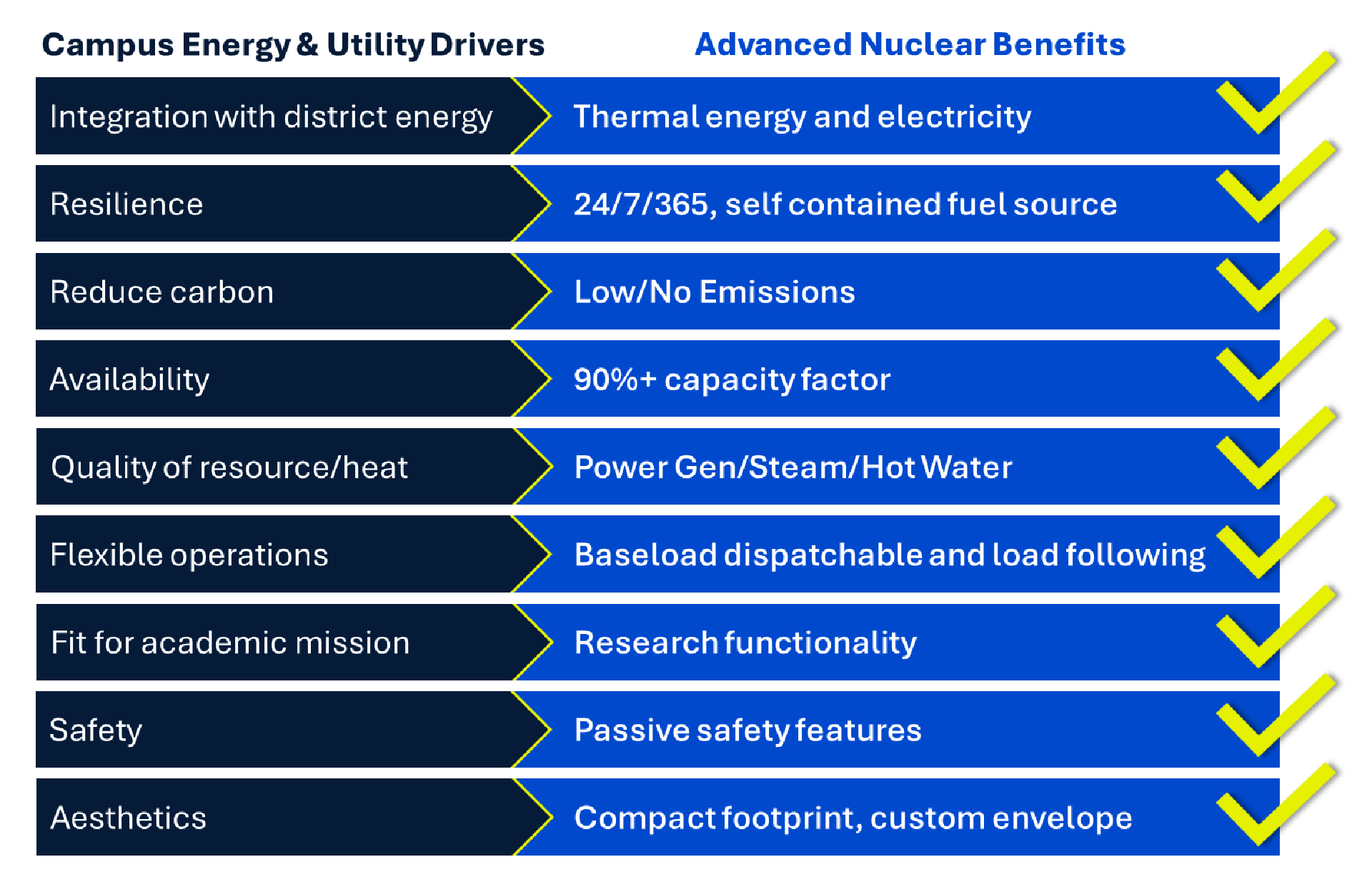
- When considering the typical needs of a district energy or campus utility infrastructure, a nuclear microreactor checks all the boxes for providing a clean, resilient energy source.
- What is needed for microreactors to be accepted and commercially deployed?
- The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has outlined key steps needed for microreactors to achieve affordability and widespread deployment in its "Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Advanced Nuclear." Important advancements needed include the following.
- Research and development. Continued innovation in reactor design, materials and safety systems involves extensive testing and validation to create viable and safe operations.
- Regulatory approval. Technologies must meet stringent safety and environmental standards, and a streamlined NRC approval and licensing process can accelerate commercialization.
- Demonstration projects. Implementing pilot first-of-a-kind projects will demonstrate the advanced nuclear’s feasibility and reliability. Initial deployments will help build confidence among stakeholders and provide valuable data to help the industry further mature.
- Financing and investment. Public and private sector investment and funding are crucial to support the development and deployment of microreactors.
- Manufacturing and supply chain development. A robust supply chain for components and materials used in microreactors is still developing. Manufacturing must also scale to meet demand.
- Market deployment. Demonstrating microreactors in various applications, including district energy, remote power applications, industrial sites and military bases, will help build customer awareness and technology acceptance.
- Policy and incentives. The government can continue to play an important role by providing incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of advanced nuclear technologies, which will, in turn, drive market growth.
- Public engagement and education. Addressing public concerns and misconceptions about nuclear energy through education and transparent communication is crucial since public trust is essential for widespread acceptance.
- The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has outlined key steps needed for microreactors to achieve affordability and widespread deployment in its "Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Advanced Nuclear." Important advancements needed include the following.
On-Demand Webinar
Complete the form below to access the webinar.
Featured Content
Nuclear Microreactors Offer Promising Future for District Energy
Meet Growing Data Center Power Demands With Reciprocating Engines
Nuclear Microreactors Could Be Zero-Carbon Solution for Campus District Energy Systems