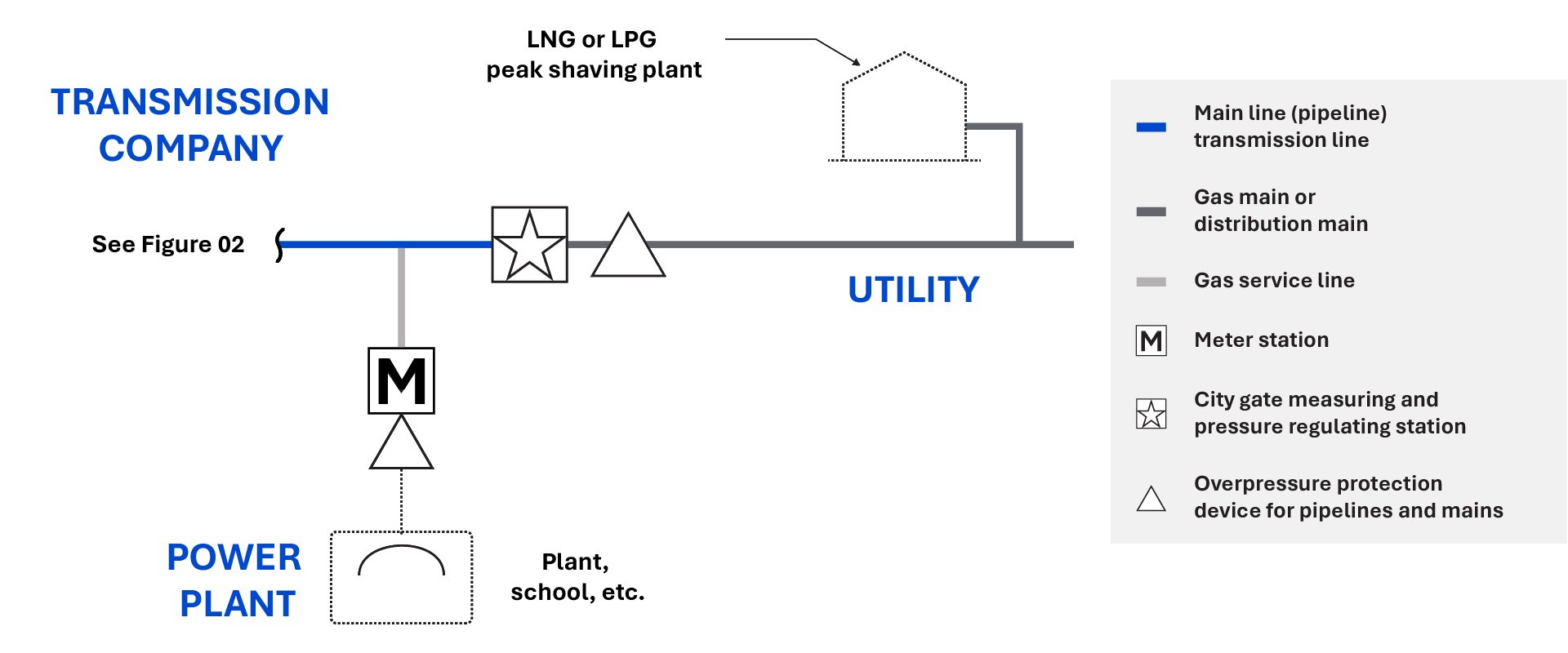
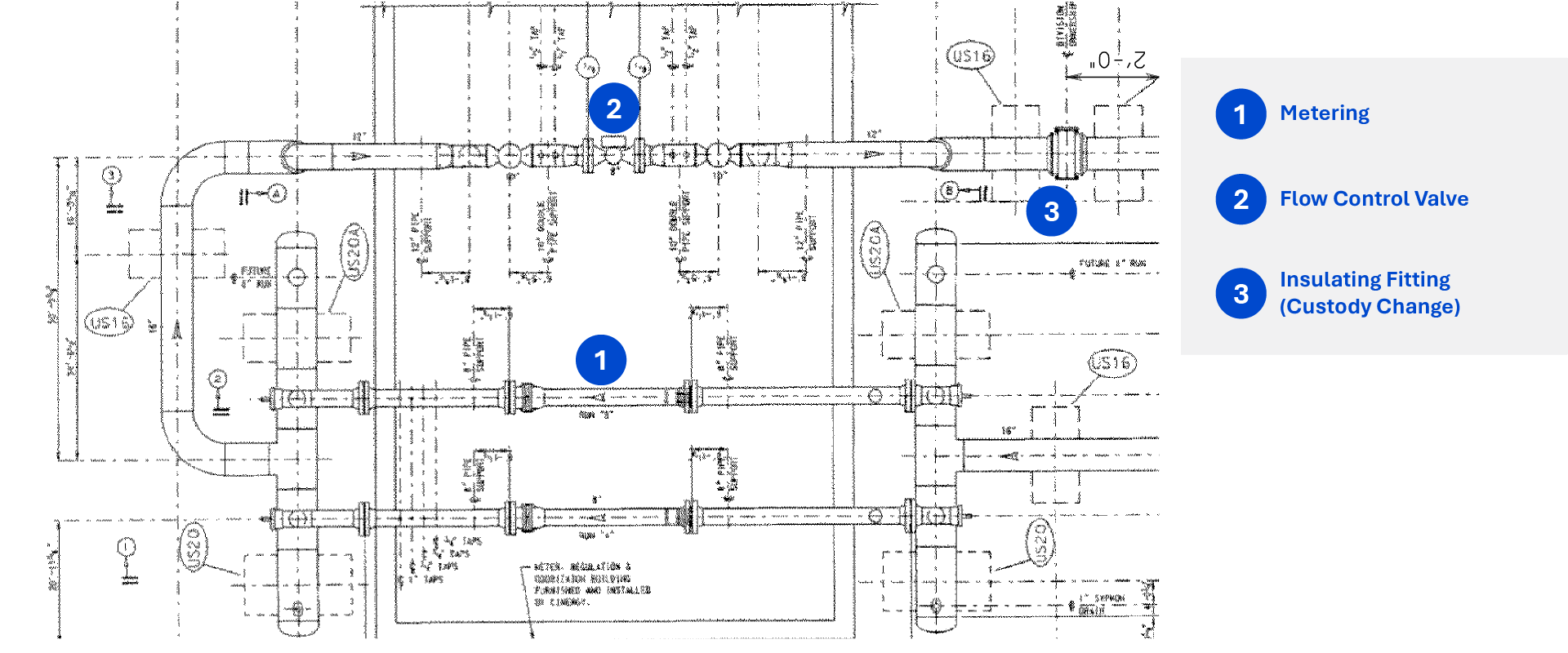
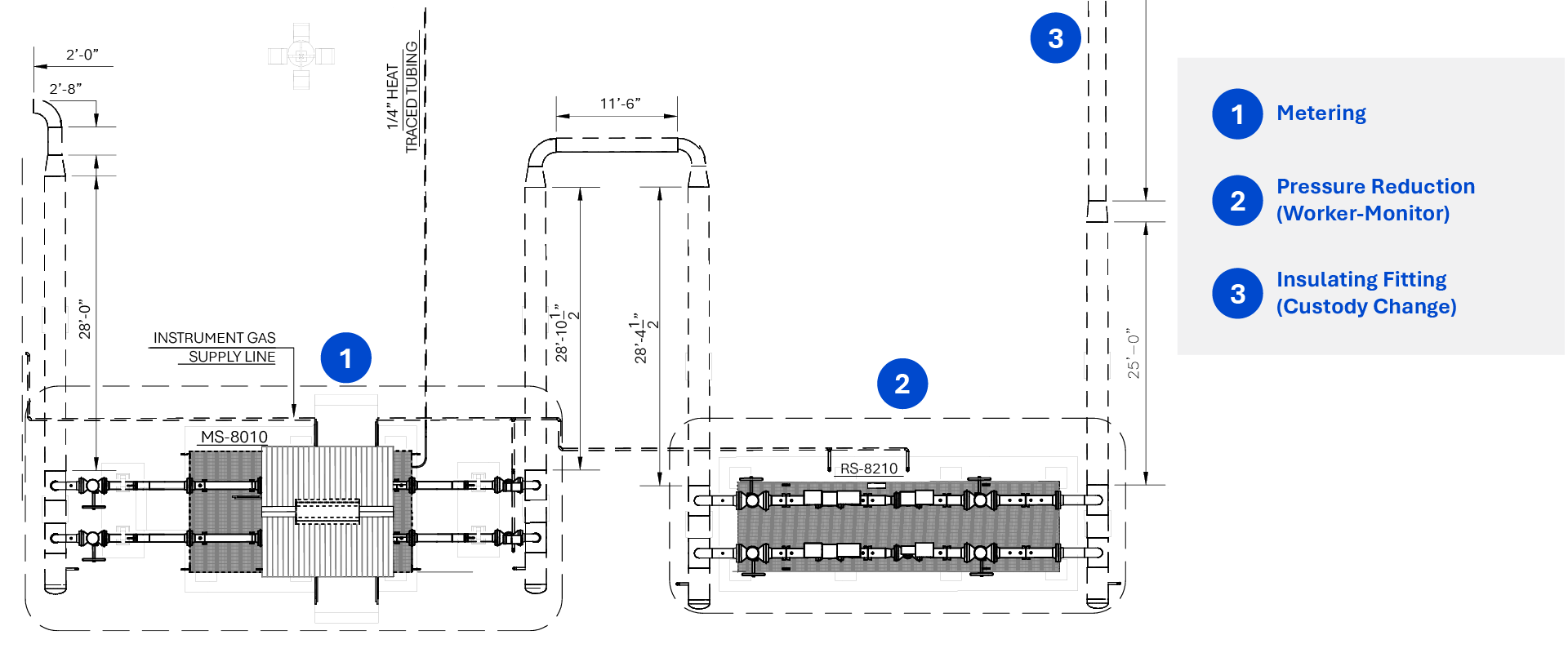
Natural gas is an essential commodity used for generating electricity, fueling vehicles, cooking and more. In the United States alone, it is supplied through networks of pipelines spread across millions of miles. Protecting these pipelines and the public from both internal and external damage is crucial because natural gas can be hazardous, and a break in the distribution network can threaten public safety and cause serious economic losses. One such challenge faced by utilities is overpressure events in their pipelines and how to properly protect against them. This paper examines redundant overpressure protection (OPP) requirements at the city gates in the U.S. and how several operators are at risk of noncompliance as states begin to enforce redundant OPP requirements specifically at the city gates.
Different OPP solutions are available in the market. It is up to each utility to evaluate its existing system and identify suitable safety devices that comply with federal regulations and safeguard the pipeline distribution network from accidents.